Java is an object-oriented programming language and you will see a lot of object oriented programming concept questions on Java interviews. The classic questions like difference between interface and abstract class are always there but from the last couple of years more sophisticated questions based upon advanced design principles and patterns are also asked tocheck OOP knowledge of the candidate. Though, Object oriented programming questions are more popular on Java interviews for 1 to 3 years experienced programmers. It makes sense as well, as these are the programmers who must know the OOP basic like Abstraction, Inheritance, Composition, Class, Object, Interface, Encapsulation etc. If you look for Java interview questions for 2 to 4 years experienced programmer, you will find lots of questions based upon OOP fundamentals like Inheritance and Encapsulation but as you gain more experience, you will see questions based upon object oriented analysis and design e.g. code a vending design machine or implement a coffeemaker in Java. These questions are more difficult and require not only true understanding of OOP fundamental but also about SOLID design principles and patterns.
OOPS Concept Interview Questions in Java
In this article, I am going to share you some OOPS concept based Java interview questions which I have collected from friends and colleagues and they have seen in various Java interviews on different companies. They are mostly asked at first few round e.g. on screening round or on the telephonic round. If you are senior Java developer then you already knowanswers of this question and I suggest you practice more on object-oriented analysis and design skill i.e. how to do code against a specification. If you are fresher and junior Java developer with 2 to 3 years experience then you must revise these questions, learn if you don't know to do well on your Java Job interviews.
Read more: http://www.java67.com/2015/12/top-30-oops-concept-interview-questions-answers-java.html#ixzz4cyux0MCO
What is method overloading in OOP or Java? (answer)
It's one of the oldest OOPS concept questions, I have seen it 10 years ago and still sees it now. When we have multiple methods with the same name but different functionality then it's called method overloading. For example. System.out.println() is overloaded as we have 6 or 7 println() method each accepting a different type of parameter.
What is method overriding in OOP or Java? (answer)
It's one of the magic of object oriented programming where the method is chose based upon an object at runtime. In order for method overriding, we need Inheritance and Polymorphism, as we need a method with the same signature in both superclass and subclass. A call to such method is resolved at runtime depending upon the actual object and not the type o variable. See the answer for more detailed discussion.
What is method hiding in Java? (answer)
When you declare two static methods with same name and signature in both superclass and subclass then they hide each other i.e. a call to the method in the subclass will call the static method declared in that class and a call to the same method is superclass is resolved to the static method declared in the super class.
Is Java a pure object oriented language? if not why? (answer)
Java is not a pure object-oriented programming language e.g. there are many things you can do without objects e.g. static methods. Also, primitive variables are not objects in Java. See the answer for a more detailed explanation.
What are rules of method overloading and overriding in Java? (answer)
One of the most important rule of method overloading in Java is that method signature should be different i.e. either the number of arguments or the type of arguments. Simply changing the return type of two methods will not result in overloading, instead compiler will throw an error. On the other hand, method overriding has more rules e.g. name and return type must be same, method signature should also be same, the overloaded method cannot throw a higher exception etc. See the answer for a full list of rules related to method overloading and overriding in Java.
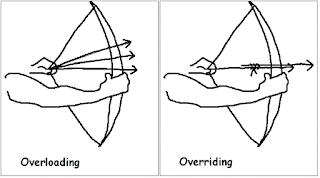
The difference between method overloading and overriding? (answer)
Several differences but the most important one is that method overloading is resolved at compile time and method overriding is resolved at runtime. The compiler only used the class information for method overloading, but it needs to know object to resolved overridden method calls. This diagram explains the difference quite well, though:
Can we overload a static method in Java? (answer)
Yes, you can overload a static method in Java. You can declare as many static methods of the same name as you wish provided all of them have different method signatures. See the answer for more detailed explanation and code example.
Can we override static method in Java? (answer)
No, you cannot override a static method because it's not bounded to an object. Instead, static methods belong to a class and resolved at compile time using the type of reference variable. But, Yes, you can declare the same static method in a subclass, that will result in method hiding i.e. if you use reference variable of type subclass then new method will be called, but if you use reference variable of superclass than old method will be called.
Can we prevent overriding a method without using the final modifier? (answer)
Yes, you can prevent the method overriding in Java without using the final modifier. In fact, there are several ways to accomplish it e.g. you can mark the method private or static, those cannot be overridden.
Can we override a private method in Java? (answer)
No, you cannot. Since the private method is only accessible and visible inside the class they are declared, it's not possible to override them in subclasses. Though, you can override them inside the inner class as they are accessible there.
What is covariant method overriding in Java? (answer)
In covariant method overriding, the overriding method can return the subclass of the object returned by original or overridden method. This concept was introduced in Java 1.5 (Tiger) version and it's very helpful in case original method is returning general type like Object class, because, then by using covariant method overriding you can return more suitable object and prevent client side type casting. One of the practical use of this concept is in when you override the clone() method in Java.
Can we change the return type of method to subclass while overriding? (answer)
Yes, you can, but only from Java 5 onward. This feature is known as co-variant method overriding and it was introduced in JDK 5 release. This is immensely helpful if original method return super-class e.g. clone() method return java.lang.Object. By using this, you can directly return the actual type, preventing client-side type casting of the result.
Can we change the argument list of an overriding method? (answer)
No, you cannot. The argument list is part of the method signature and both overriding and overridden method must have the same signature.
Can we override a method which throws runtime exception without throws clause? (answer)
Yes, there is no restriction on unchecked exception while overriding. On the other hand, in the case of checked exception, an overriding exception cannot throw a checked exception which comes higher in type hierarchy e.g. if original method is throwing IOException than overriding method cannot throw java.lang.Exception or java.lang.Throwable.
How do you call superclass version of an overriding method in sub class? (answer)
You can call a superclass version of an overriding method in the subclass by using super keyword. For example to call the toString() method from java.lang.Object class you can call super.toString().
Can we override a non-static method as static in Java? (answer)
Yes, you can override the non-static method in Java, no problem on them but it should not be private or final :)
Can we override the final method in Java? (answer)
No, you cannot override a final method in Java, final keyword with the method is to prevent method overriding. You use final when you don't want subclass changing the logic of your method by overriding it due to security reason. This is why String class is final in Java. This concept is also used in template design pattern where template method is made final to prevent overriding.
Can we have a non-abstract method inside interface? (answer)
From Java 8 onward you can have a non-abstract method inside interface, prior to that it was not allowed as all method was implicitly public abstract. From JDK 8, you can add static and default method inside an interface.
What is the default method of Java 8? (answer)
Default method, also known as extension method are new types of the method which you can add on the interface now. These method has implementation and intended to be used by default. By using this method, JDK 8 managed to provide common functionality related to lambda expression and stream API without breaking all the clients which implement their interfaces. If you look Java 8 API documentation you will find several useful default method on key Java interface like Iterator, Map etc.
What is an abstract class in Java? (answer)
An abstract class is a class which is incomplete. You cannot create an instance of an abstract class in Java. They are provided to define default behavior and ensured that client of that class should adore to those contract which are defined inside the abstract class. In order to use it, you must extend and implement their abstract methods. BTW, in Java a class can be abstract without specifying any abstract method.
What is an interface in Java? What is the real user of an interface? (answer)
Like an abstract class, the interface is also there to specify the contract of an API. It supports OOP abstraction concept as it defines only abstract behavior. It will tell that your program will give output but how is left to implementors. The real use of the interface to define types to leverage Polymorphism. See the answer for more detailed explanation and discussion.
The difference between Abstract class and interface? (answer)
In Java, the key difference is that abstract class can contain non-abstract method but the interface cannot, but from Java 8 onward interface can also contain static and default methods which are non-abstract. See the answer for more detailed discussion as I have described a lot of points there.
Can we make a class abstract without an abstract method? (answer)
Yes, just add abstract keyword on the class definition and your class will become abstract.
Can we make a class both final and abstract at the same time? (answer)
No, you cannot apply both final and abstract keyword at the class same time because they are exactly opposite of each other. A final class in Java cannot be extended and you cannot use an abstract class without extending and making it a concrete class. As per Java specification, the compiler will throw an error if you try to make a class abstract and final at the same time.
Can we overload or override the main method in Java? (answer)
No, since main() is a static method, you can only overload it, you cannot override it because the static method is resolved at compile time without needing object information hence we cannot override the main method in Java.
What is the difference between Polymorphism, Overloading, and Overriding? (answer)
This is slight tricky OOP concept question because Polymorphism is the real concept behind on both Overloading and Overriding. Overloading is compile time Polymorphism and Overriding are runtime Polymorphism.
Can an interface extend more than one interface in Java?
Yes, an interface can extend more than one interface in Java, it's perfectly valid.
Can a class extend more than one class in Java?
No, a class can only extend another class because Java doesn't support multiple inheritances but yes, it can implement multiple interfaces.
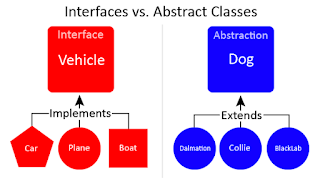
What is the difference between abstraction and polymorphism in Java? (answer)
Abstraction generalizes the concept and Polymorphism allow you to use different implementation without changing your code. This diagram explains the abstraction quite well, though:
Object Oriented design principle and pattern Interview Questions
Now let's see some OOPS concept questions based upon the SOLID design principles and GOF design patterns which take advantage of OOPS concept discussed here.
What problem is solved by Strategy pattern in Java? (answer)
Strategy pattern allows you to introduce new algorithm or new strategy without changing the code which uses that algorithm. For example, the Collections.sort() method which sorts the list of the object uses Strategy pattern to compare object. Since every object uses different comparison strategy you can compare various object differently without changing sort method.
Which OOP concept Decorator design Pattern is based upon? (answer)
Decorator pattern takes advantage of Composition to provide new features without modifying the original class. A very good to-the-point question for the telephonic round. This is quite clear from UML diagram of Decorator pattern, as you can see the Component is associated with Decorator.
When to use Singleton design pattern in Java? (answer)
When you need just one instance of a class and wants that to be globally available then you can use Singleton pattern. It's not free of cost though because it increase coupling between classes and make them hard to test. This is one of the oldest design pattern questions from Java interviews. Please see the answer for more detailed discussion.
When you need just one instance of a class and wants that to be globally available then you can use Singleton pattern. It's not free of cost though because it increase coupling between classes and make them hard to test. This is one of the oldest design pattern questions from Java interviews. Please see the answer for more detailed discussion.
What is the difference between State and Strategy Pattern? (answer)
Though the structure or class diagram of State and Strategy pattern is same, their intent is completely different. State pattern is used to do something specific depending upon state while Strategy allows you to switch between algorithms without changing the code which uses it.
What is the difference between Association, Aggregation, and Composition in OOP? (answer)
When an object is related to another object it called association. It has two forms, aggregation, and composition. the former is the loose form of association where the related object can survive individual while later is a stronger form of association where a related object cannot survive individually. For example, the city is an aggregation of people but is the composition of body parts.
What is the difference between Decorator, Proxy and Adapter pattern in Java? (answer)
Again they look similar because their structure or class diagram is very similar but their intent is quite different. Decorator adds additional functionality without touching the class, Proxy provides access control and Adapter is used to make two incompatible interfaces work together.
What is the 5 objects oriented design principle from SOLID? (answer)
SOLID is the term given by Uncle Bob in his classic book, the Clean Code, one of the must-read books for programmers. In SOLID each character stands for one design principle:
S for Single Responsibility Principle
O for Open closed design principle
L for Liskov substitution principle
I for Interface segregation principle
D for Dependency inversion principle
What is the difference between Composition and Inheritance in OOP? (answer)
This is another great OOPS concept question because it test what matters, both of them are very important from a class design perspective. Though, both Composition and Inheritance allows you to reuse code, former is more flexible than later. Composition allows the class to get an additional feature at runtime, but Inheritance is static. You can not change the feature at runtime by substitution new implementation. See the answer for more detailed discussion.
That's all about in this list of object oriented programming or OOPS concept interview questions. We have seen questions from various OOPS concept e.g. Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Composition, Aggregation, Association, Class, Object and Interface etc. We have also seen questions from Object oriented design principles also known as SOLID principles and GOF design patterns like Strategy, State, and Factory, which are based upon Object oriented programming concept and OOP design principle. But, as I said, if you are senior Java developer then you focus more on object-oriented analysis and design and learn how to code against a requirement using all your OOP knowledge. You can also read Cracking the Coding Interview, 6th Edition to for more Object Oriented Programming questions.


No comments:
Post a Comment